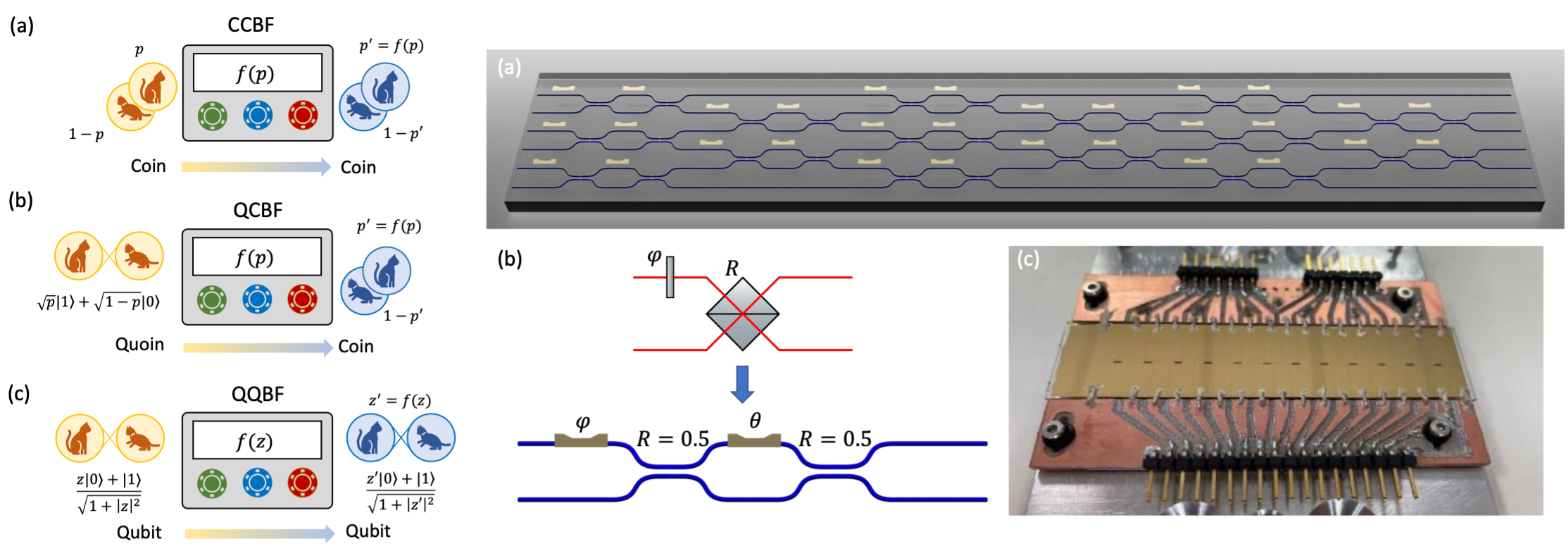
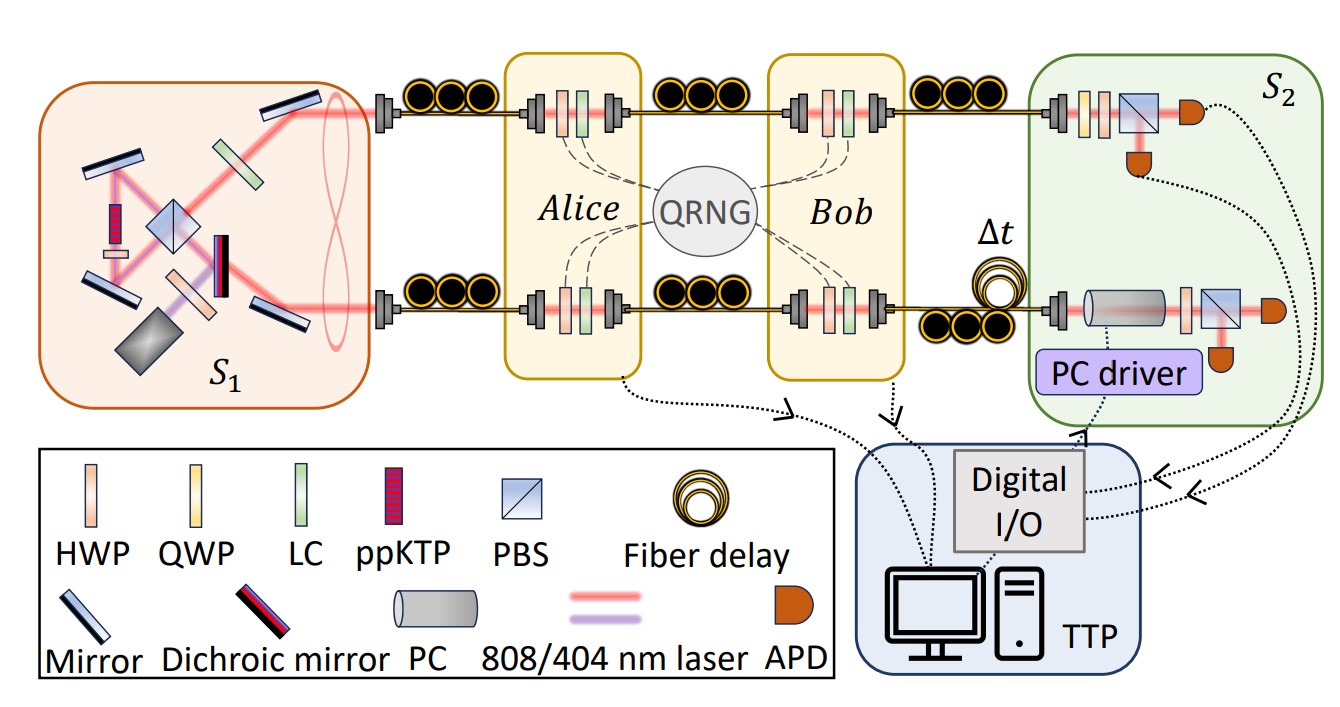
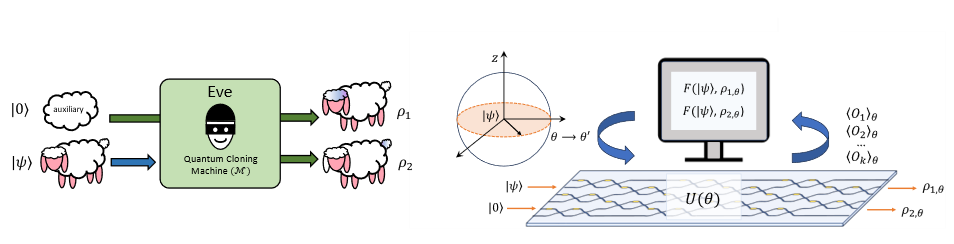
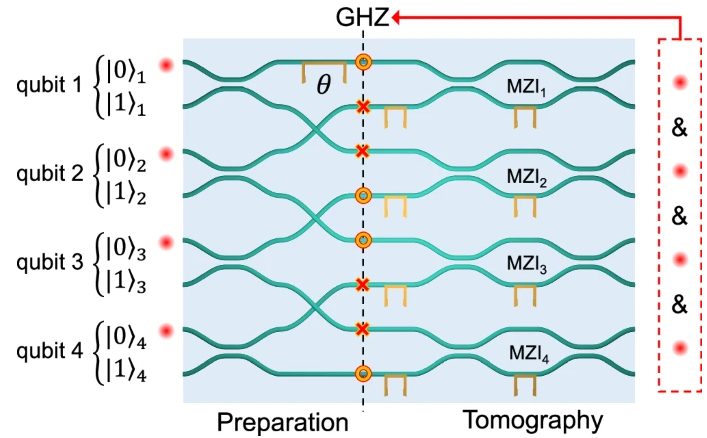
“Modular Quantum-to-Quantum Bernoulli Factory in an Integrated Photonic Processor” just published in Nature Photonics
Generating and manipulating randomness is essential for numerous information technology applications, and quantum mechanics has been shown to offer distinct advantages in this area. A notable model for randomness manipulation is the Bernoulli factory, which enables the controlled adjustment of the bias in Bernoulli random processes. Initially, this framework was explored entirely within a classical … Leggi tutto